SQL you know but type safe parameterized, expressive & portable
litdb contains LINQ-like type-safe SQL builders for TypeScript/JavaScript for writing type-safe expressive SQL that's parameterized & portable across SQLite, MySQL & PostgreSQL
SQL-like
No need to learn a new query language, litdb lets you write familiar SQL you know
using its type-safe expressions and query builders that's safe by default.
APIs are designed to keep a close affinity to SQL making it clear what SQL is being generated,
expressions utilize tagged templates to take away the tedium of maintaining table and column
references, parameterizing values and catering for different SQL dialects to retain the
expressive freedom of SQL, but portable across multiple RDBMS's.
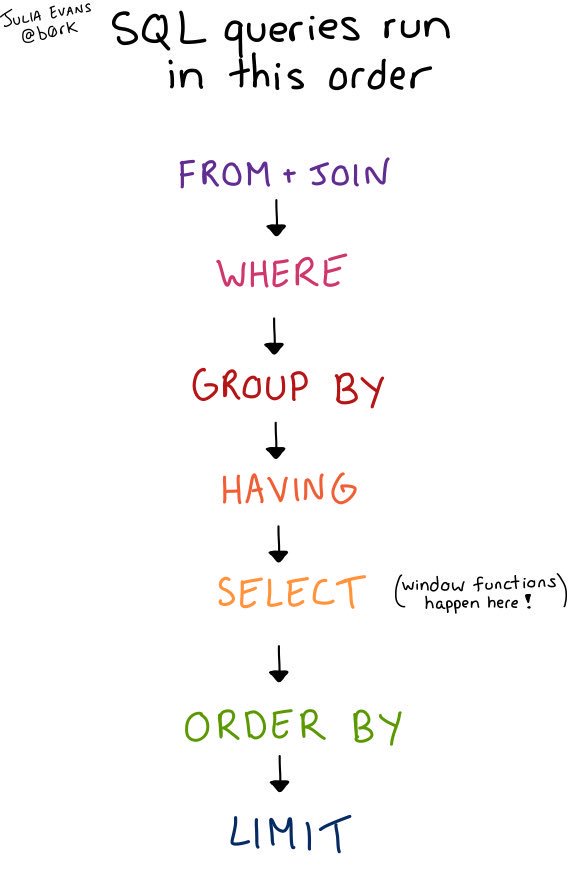
The primary difference between SQL is how queries are constructed, where the SELECT Query Builder
directs queries to be constructed in
the order they're run,
by specifying the data sources first, i.e. the FROM table first, followed by any JOINs
(just like LINQ)
which allows litdb query builders to provide type safety and intellisense for the rest of the query.
Install
To use litdb with your favorite ORM, no driver is required. Just use the litdb package directly:
npm install litdb
litdb is also available as a module, where it can be used directly in the browser:
<script type="module">
import { sqlite as $ } from "https://unpkg.com/litdb/dist/index.min.js"
const { sql, params } = $.from(Contact).select(c => $`${c.name}`).build()
</script>
To get the most out of litdb we recommend using text editors that supports TypeScript definitions
(e.g. VS Code, JetBrains IDEs, neovim, etc.)
LitDB Drivers
Lightweight drivers with native support for its typed SQL Builders and parameterized SQL Expressions are also available for the popular databases:
Bun SQLite
Use with Bun's native SQLite3 driver (requires Bun):
bun install @litdb/bun-sqlite
Node better-sqlite
Use with better-sqlite3 (requires Node.js):
npm install @litdb/better-sqlite
PostgreSQL
Use with the postgres.js client:
npm install @litdb/postgres
MySQL
Use with the mysql2 client:
npm install @litdb/mysql2
Request a Driver
If you'd like to see a driver for a specific client, please open or vote for a feature request on litdb's GitHub Discussions.
Driver Usage
The litdb Drivers provide a unified interface for executing custom parameterized SQL, SQL Builders and SQL Fragments for their respective RDBMS. They're lightweight data adapters providing convenience APIs for executing SQL with named and positional parameters. They can be used without litdb SQL Builders, but offer the most value when used together.
The same APIs are available across all drivers, so you can easily switch between them. They include both sync APIs recommended for SQLite libraries that use SQLite's native blocking APIs, whilst async APIs should be used for all other remote databases, e.g. PostgreSQL and MySQL.
Example of using the Bun SQLite driver:
db.ts
import { connect } from "@litdb/bun-sqlite"
export const connection = connect("app.db") // WAL enabled by default
export const { $, sync:db, async, native } = connection
TIP
When needed use native to access underlying driver (e.g. bun:sqlite Database)
app.ts
import { $, db } from "./db"
import { Contact } from "./models"
db.dropTable(Contact)
db.createTable(Contact)
db.insertAll([
new Contact({ name:"John Doe", email:"[email protected]" }),
new Contact({ name:"Jane Doe", email:"[email protected]" }),
])
const janeEmail = '[email protected]'
const jane = db.one<Contact>($.from(Contact).where(c => $`${c.email} = ${janeEmail}`))!
// Insert examples
const { lastInsertRowid: bobId } = db.insert(new Contact({ name:"Bob", email:"[email protected]" }))
const { lastInsertRowid } = db.exec`INSERT INTO Contact(name,email) VALUES ('Jo','[email protected]')`
const name = 'Alice', email = '[email protected]'
db.exec`INSERT INTO Contact(name,email) VALUES (${name}, ${email})`
// Typed SQL fragment with named param example
const hasId = <Table extends { id:number }>(id:number|bigint) =>
(x:Table) => $.sql($`${x.id} = $id`, { id })
const contacts = db.all($.from(Contact).into(Contact)) // => Contact[]
const bob = db.one($.from(Contact).where(hasId(bobId)).into(Contact)) // => Contact
const contactsCount = db.value($.from(Contact).select`COUNT(*)`) // => number
const emails = db.column($.from(Contact).select(c => $`${c.email}`)) // => string[]
const contactsArray = db.arrays($.from(Contact)) // => any[][]
const bobArray = db.array($.from(Contact).where(hasId(bobId))) // => any[]
// Update examples
jane.email = '[email protected]'
db.update(jane) // Update all properties
db.update(jane, { onlyProps:['email'] }) // Update only email
db.exec($.update(Contact).set({ email:jane.email }).where(hasId(jane.id))) // query builder
// Delete examples
db.delete(jane)
db.exec($.deleteFrom(Contact).where(hasId(jane.id))) // query builder
Same source is compatible with other sync drivers, e.g. can replace @litdb/bun-sqlite with @litdb/better-sqlite to use
with better-sqlite. See also async usage docs for postgres and mysql2.
Type Safe
Get productive intelli-sense for quickly accessing properties that exist your data model or design-time type-checking and compile-time static analysis errors for those that don't.
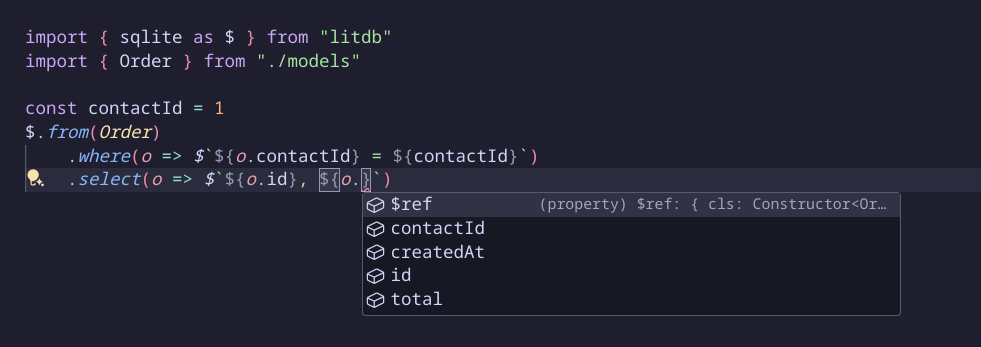
Only reference table and columns that are included in your query, quickly identify missing tables, columns and any typos:
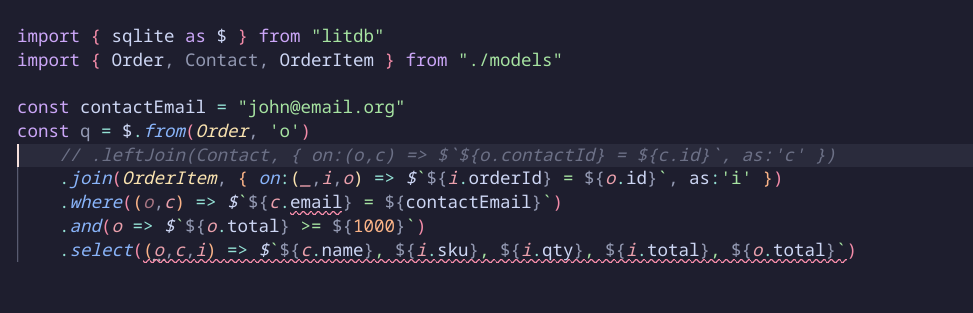
Safe Refactoring
All references are statically typed to your models so you can safely refactor with confidence!
Composable
Queries are highly composable where SQL Fragments can embed and merge the SQL and parameters of other Fragments
For complex multi-part queries external references can be used across multiple Query Builders and SQL fragments to easily create and compose multiple complex queries with shared references.
SQL Builders and SQL fragments can be embedded inside other query builders utilizing the full expressiveness of SQL where their SQL and parameters are merged into the parent query.